North America DC Charger Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, By Power Output (Upto 150 kW and Above 150 kW), By Connector (NACS, CCS, and CHAdeMO and Others), By Location (Destination and Enroute), and Country Forecast, 2025-2040
KEY MARKET INSIGHTS
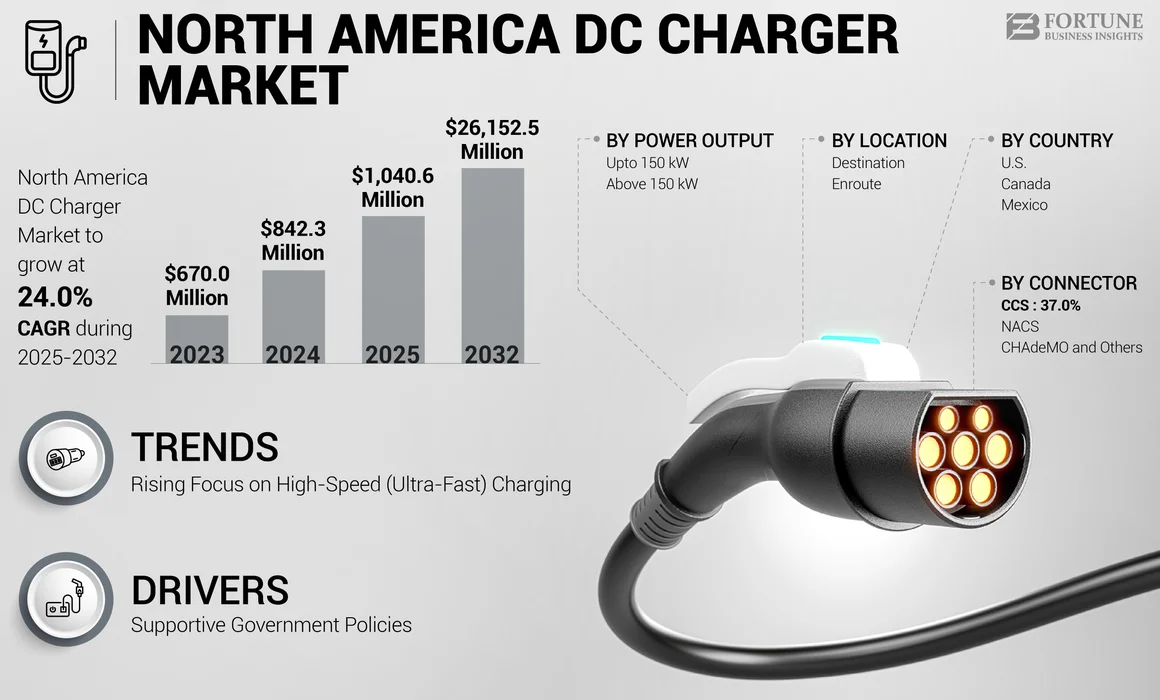
The North America DC Charger market size was valued at USD 842.3 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 1,040.6 million in 2025 to USD 26,152.5 million by 2040, exhibiting a CAGR of 24.0% during the forecast period.
DC fast chargers are a critical part of EV infrastructure as they cater to the growing need for various EV charging solutions that support longer trips and reduce waiting times. Unlike traditional AC chargers, which can take hours to recharge a vehicle, DC fast chargers can charge vehicles in less time. This quick turnaround time is essential for EV drivers who need a convenient and efficient travel experience, especially as the range of EVs improves but still requires recharging during long-distance trips.
Many EV manufacturers are ramping up production and expanding their vehicle lineups, including budget-friendly models and high-performance electric vehicles. This increased vehicle availability is creating a broader consumer base, and as more EVs hit the road, the infrastructure to support them, including DC fast chargers, is expanding. Thus, the growth of EV adoption is a key driver of the growing demand for DC chargers in North America. Market growth is characterized by supportive government policies for the acceleration of the electric vehicle (EV) industry. Key players in the market include Tesla, ChargePoint, Blink, Electrify, ABB, EVgo, and EVBox.
EV adoption is experiencing significant growth in North America, driven by a combination of factors, including consumer interest, governmental policies, and advances in EV technology. As more consumers opt for EVs due to their environmental benefits, lower operating costs, and the growing availability of models across different price points, the demand for EV infrastructure, particularly fast-charging solutions, is increasing.
Download Free sample to learn more about this report.
Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Supportive Government Policies to Drive Market Growth
Government policies and regulations are among the primary catalysts driving the rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and, consequently, the increasing need for DC fast chargers in North America. In an effort to combat climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and support the transition to clean energy, governments at the federal and state levels have introduced various incentives, subsidies, and regulations to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles.
In the U.S., federal tax credits help reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable for a wider range of consumers. At the state level, incentives such as purchase rebates and access to carpool lanes for EV drivers further promote adoption. These incentives reduce financial barriers for consumers and accelerate the transition to electric mobility. Furthermore, there are growing legislative pressures for automakers, requiring a transition toward more environmentally friendly technologies. Policies such as California’s Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) mandate, which requires automakers to sell a certain percentage of zero-emission vehicles, and broader federal commitments to reducing carbon emissions are key drivers of this transition. These policies indirectly boost the need for EV charging infrastructure to keep up with the rise in EVs on the road.
Market Restraints
High Infrastructure Costs and Power Supply Issues May Hamper Market Growth
The installation of DC fast chargers requires significant capital investment, particularly compared to Level 2 chargers, which are slower but more affordable. The cost of a direct current fast chargers (DCFC) unit varies significantly, depending on its power capacity, making it a substantial financial commitment for businesses and municipalities. In addition to the cost of the charging units themselves, additional expenses arise from installation-related factors, such as electrical grid upgrades, land acquisition, and the setup of necessary electrical infrastructure.
DC fast chargers require more frequent maintenance than slower chargers due to the higher power levels and more complex components involved. This leads to increased long-term operational costs, which can make them less attractive investments for businesses or public entities seeking a strong return on investment.
Another challenge for the North America DC Charger market growth is the lack of standardized grid compatibility across utilities and energy providers, which can complicate DCFC deployments. The absence of uniform regulations on how charging stations should be connected to the grid results in inefficiencies and delays, further hindering the expansion of charging infrastructure.
Market Opportunities
Expansion of Charging Networks Along Highways and Major Routes to Support Market Growth
One of the significant challenges for EV owners is ensuring sufficient charging stations are available along key travel routes. As EV adoption grows, there is a substantial opportunity to expand DC fast charger installations along major highways and long-distance travel corridors. Under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, the U.S. government allocated USD 7.5 billion for building a nationwide network of EV chargers, prioritizing DC fast chargers. This investment helps establish a network of high-speed chargers that reduce range anxiety for EV drivers traveling across the country. Companies can partner with governments and private enterprises to develop high-speed charging hubs along well-traveled routes, such as interstates, highways, and major urban centers. Strategically placed charging locations will support long-distance EV travel, making electric vehicles more practical for consumers who need rapid recharging.
Market Challenges
Power Supply Issues May Pose Challenge to Product Demand
DC fast chargers require significant power, especially those that can charge EVs at higher speeds (150 kW or more). In many locations, the electrical grid lacks the capacity to handle the additional load of multiple DC chargers operating simultaneously, particularly in areas with limited or outdated infrastructure. This can result in power shortages, brownouts, or other grid reliability issues. Upgrading the local grid to meet higher power requirements can be expensive and time-consuming, which slows down the widespread deployment of DC fast chargers.
Another concern is that many DC fast chargers still rely on electricity generated from non-renewable energy sources. If the EV charging network remains reliant on fossil fuels or non-sustainable sources, it undermines the environmental benefits of EV adoption. There is an increasing pressure to power DC chargers with renewable energy; however, the transition to clean energy can be expensive and logistically challenging, particularly in remote or less-developed regions.
North America DC Charger Market Trends
Rising Focus on High-Speed (Ultra-Fast) Charging to Drive Market Growth
As the EV market evolves, there is a growing demand for ultra-fast chargers. These chargers can significantly reduce charging times to as little as 15 minutes for compatible EVs, making long-distance travel much more convenient and attractive for consumers. The development of high-power DC fast chargers capable of ultra-fast charging is a key trend in the industry. The demand for ultra-fast DC chargers is on the rise, driven by the increasing range and faster charging capabilities of modern EVs. Companies such as Tesla, Electrify America, and EVgo are expanding their networks to meet the needs of long-range EV users.
Many manufacturers are moving toward modular charging systems, which allow for easier upgrades and ensure chargers can keep pace with evolving EV technology and consumer needs. Modular designs also make infrastructure expansion more cost-effective and adaptable to future needs. Charging station operators are utilizing big data and machine learning algorithms to analyze usage patterns, optimize EV charging station locations, predict demand, and improve customer experience. For example, data analytics can help identify peak charging times, anticipate maintenance needs, and personalize services for users, improving the efficiency and reliability of fast-charging networks.
Impact of COVID-19
Production Slowdown and Supply Chain Roadblocks the Market Growth
The electric vehicle (EV) market in North America gained momentum pre-2020. Government incentives, growing consumer awareness, and increasing EV model availability fueled the demand for DC fast chargers, vital infrastructure for long-distance travel, and convenient charging for apartment dwellers. However, the COVID-19 pandemic hit, throwing the burgeoning market a curveball that significantly altered its trajectory. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and widespread economic uncertainty kept people at home, halting non-essential travel. Global manufacturing shutdowns led to shortages of critical components, delaying DC charger production and maintenance. These disruptions resulted in project delays, increased costs, and a slower rollout of much-needed charging infrastructure.
Despite these setbacks, the downturn was short-lived. As restrictions eased and economies reopened, the EV market, and consequently the DC charger market, began to recover. The pandemic accelerated a shift toward greater environmental awareness and cleaner transportation options. With reductions in emissions during lockdowns, EVs gained appeal as a sustainable alternative. Continued government incentives and growing model availability further drove EV sales.
The pandemic highlighted the importance of reliable and accessible charging infrastructure. The initial decline in public EV charging utilization highlighted the need for more strategically placed charging stations, particularly in underserved areas. This realization renewed interest in DC charger deployment, focusing on addressing gaps in the existing network to support long-term EV growth.
Segmentation Analysis
By Power Output
Above 150 kW Segment to Display Highest CAGR Due to Advancements in Smart Charging
On the basis of power output, the market is segmented into upto 150 kW and above 150 kW.
The above 150 kW segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period from 2025 to 2040. Range anxiety and long charging times remain key concerns for EV owners, especially during long-distance travel. High-power chargers above 150 kW (e.g., 350 kW or more) are crucial for highway high-speed charging, enabling long-haul drivers to quickly downtime and continue their journeys efficiently. Advancements in smart charging, including vehicle-to-grid technology, could help these stations to feed energy back into the grid and stabilize energy demand during peak periods.
The upto 150 kW segment captured a significant market share of 75.7% in 2024. Various federal and state-level programs in the U.S. are investing heavily in EV infrastructure to support sustainability and climate goals. The U.S. government’s EV charging infrastructure funding, especially under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), aims to deploy charging stations nationwide, with a focus on high-power DC fast chargers. Many states, such as California, have stringent emissions targets and offer incentives, including rebates, tax incentives, and other benefits, to encourage EV adoption and the installation of DC fast chargers. Companies such as Tesla and Electrify America are rapidly expanding their fast-charging networks. The development of 150 kW chargers allows charging speed, making networks more competitive and appealing to users.
By Connector
NACS Segment Led the Market due to the Established Supercharger Network
Based on the connector, the market is divided into NACS, CCS, and CHAdeMO and others.
The NACS segment dominated the market in 2024, capturing the majority of the North America DC Charger market share. The most significant driver behind the NACS is Tesla's dominant market presence in the North American EV market. Tesla owners have long enjoyed access to the extensive Supercharger network, known for its reliability and ease of use. This well-established infrastructure, coupled with the popularity of Tesla vehicles, has made a strong case for other manufacturers and charging providers to adopt NACS compatibility. By adopting NACS, companies can tap into Tesla’s large and expanding customer base, expanding their reach and revenue streams. The shift toward NACS has been accelerated by major automakers and charging network operators embracing the standard. This commitment reinforces NACS as the dominant standard for DC charging.
The CCS segment is expected to grow steadily during the forecast period. CCS connectors offer high power capabilities, making them ideal for fast-charging networks. With a maximum power output of up to 350 kW, CCS connectors enable faster charging times compared to lower-powered alternatives. These capabilities are crucial for long-distance EV travel and help alleviate range anxiety among EV drivers.
To know how our report can help streamline your business, Speak to Analyst
By Location
Destination Segment Led the Market due to Sustainability Branding
Based on location, the market is categorized into destination and enroute.
The destination segment captured a major share of the North America DC charger market. Retail spaces are inherently well-suited for DC fast charger deployment due to their accessibility, proximity to major roadways, and existing electrical infrastructure. Strategic placement within parking lots, particularly near entrances, maximize visibility and accessibility. Furthermore, retailers can generate revenue directly from charging fees, creating a new income stream, and offsetting the initial investment in infrastructure. Charging rates can be adjusted based on market demand and energy costs, optimizing profitability. In today's environmentally conscious market, retailers are increasingly focused on demonstrating their commitment to sustainability. Installing DC fast chargers sends a clear message to consumers that the business is actively contributing to a cleaner future. This positive brand image can resonate deeply with environmentally aware shoppers, enhancing brand loyalty and attracting new customers who value sustainability initiatives.
The enroute segment will grow steadily during the forecast period. The primary driver is the need to alleviate "range anxiety," the fear of running out of battery charge during a trip. While the EV range continues to improve, the perception of a limited range can still deter potential buyers. Strategically located DC fast chargers along highways provide reassurance and empower drivers to embark on longer journeys confidently. These chargers allow quick battery replenishment, typically adding significant range in 30-60 minutes, allowing drivers to continue their travels with minimal delays. This is crucial for attracting new EV adopters and fostering a more positive overall experience.
North America DC Charger Market Country Outlook
U.S.
The U.S. is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period. The federal government is playing a pivotal role in accelerating DC charger deployment through various initiatives. The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, signed into law in 2021, allocates significant funding for EV charging infrastructure, specifically targeting the development of a national network of fast chargers along major highways. Programs such as the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program provide states with funding to strategically deploy DCFCs in locations that are accessible, reliable, and convenient for drivers.
Canada
Canada held a considerable market share in 2024. Initiatives such as the Zero Emission Vehicle Infrastructure Program (ZEVIP) provide significant financial support for the installation of EV chargers, prioritizing publicly accessible DC fast chargers in strategic locations. This reduces the financial burden on businesses and municipalities, making it more attractive to invest in charging infrastructure. As more Canadians embrace electric vehicles, the need for convenient and reliable charging options increases, particularly for long-distance travel. DC fast chargers address this need by significantly faster charging times than Level 2 chargers, enabling drivers to recharge and continue their journey quickly.
Mexico
Mexico is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The country is witnessing a gradual yet significant shift in its transportation landscape. While electric vehicle (EV) adoption is still in its nascent stages compared to global leaders, the demand for Direct Current (DC) fast chargers is surging, signaling a growing interest in EVs and the need for a more robust charging infrastructure. While Mexico's EV incentives are still developing, certain regional and national initiatives are beginning to encourage EV adoption. These incentives often include tax breaks and subsidies for charging infrastructure, further fueling the demand for DC chargers.
Competitive Landscape
Key Market Players
Product Differentiation and Development to Form the Basis of Business Expansion
The North America DC charger market is highly competitive, with several players holding a strong foothold. These players have adopted various strategies such as partnerships, contracts, acquisitions, and collaborations to gain a competitive advantage. The competition is intense, with players competing on multiple factors, such as price, quality, features, and brand reputation. Moreover, the market is subject to rapid technological advancements, further intensifying competition among players.
List of Key North America DC Charger Companies Profiled:
- Tesla (U.S.)
- ChargePoint Inc. (U.S.)
- Blink Charging Co (U.S.)
- Electrify America (U.S.)
- EVgo (U.S.)
- EVBox (Netherlands)
- Francis Energy (U.S.)
- ABB (Switzerland)
- United Chargers Inc. (U.S.)
- Kempower (Finland)
Key Industry Developments
- March 2025 – Tesla collaborated with Steak ‘n Shake to install over 100 Supercharger stations at the fast-food chain's U.S. locations. This partnership emerged from a recent exchange on social media between Elon Musk and Steak ‘n Shake's official account, where the restaurant proposed the idea. Currently, Tesla has confirmed six sites and has more than 20 locations under design review. This collaboration aims to enhance charging convenience for Tesla drivers while increasing foot traffic for Steak ‘n Shake's locations, making it a mutually beneficial arrangement.
- March 2025 – EVgo Inc. and Toyota Motor North America jointly launch their inaugural DC fast charging (DCFC) stations in Baldwin Park and Sacramento, California, under Toyota’s “Empact” vision. These co-branded stations, operated by EVgo, feature 350kW chargers capable of simultaneously serving up to eight vehicles.
- December 2024 – ChargePoint and GM announced plans to expand EV infrastructure across the U.S. The collaboration aimed to install hundreds of ultra-fast charging ports at strategic locations across the U.S., featuring the latest innovations in EV charging. This initiative is designed to improve charger availability and help EV drivers get back on the road faster than ever.
- December 2024 – Electrify America signed a contract with Costco Wholesale to deploy new fast-charging Stations at select locations. These stations will feature Hyper-Fast chargers with speeds of up to 350 kW, meeting the growing demand for open and convenient fast charging.
- September 2024 – General Motors (GM) developed a GM-approved NACS DC adapter to provide its customers access to Tesla superchargers across North America. The product is available for USD 225 via GM’s vehicle brand apps. This move expands GM customers' access to more than 231,800 public Level 2 and DC fast chargers in the U.S. and Canada., improving charging accessibility.
Investment Analysis and Opportunities
Favorable Trends Associated with Ultra-Fast Charging to Generate Opportunities for Market Growth
Investment analysis in the ultra-fast DCFC sector requires a multifaceted approach. Factors such as demographics, traffic patterns, grid capacity, utility costs, and the presence of competing charging networks all play a crucial role in determining the financial viability of a charging station. A thorough understanding of local regulations and permitting processes is also paramount, as these factors can significantly impact project timelines and costs. Furthermore, investors must consider the technological advancements in charging hardware and software to ensure that selected solutions are future-proof and capable of meeting the evolving needs of the EV market.
Several key opportunities are emerging within the North American ultra-fast DCFC landscape. Firstly, strategic partnerships between charging network operators, automakers, and retail businesses can create mutually beneficial ecosystems. Automakers can incentivize the adoption of EVs by offering complimentary charging credits, while retailers can attract EV drivers to their locations, increasing foot traffic and sales. Secondly, the deployment of DCFC stations along major highway corridors is essential for facilitating long-distance EV travel. These stations typically experience higher utilization rates and serve as vital hubs for the growing EV community.
Report Coverage
The North America DC Charger market report analyze the market in-depth and highlights crucial aspects such as prominent companies, market segmentation, competitive landscape, and technology adoption. Besides this, the market research report provides insights into the DC chargers market trends and highlights significant industry developments. In addition to the aspects mentioned earlier, the report encompasses several factors contributing to the market growth over recent years.
Request for Customization to gain extensive market insights.
Report Scope & Segmentation
|
ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
|
Study Period |
2019-2040 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Estimated Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2040 |
|
Historical Period |
2019-2023 |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 24.0% from 2025 to 2040 |
|
Unit |
Value (USD Million) |
|
Segmentation |
By Power Output
By Connector
By Location
By Country
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Fortune Business Insights says that the market size was USD 842.3 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 26,152.5 million by 2040.
The market will exhibit a CAGR of 24.0% over the forecast period (2025-2040).
By connector, the NACS segment dominated the market in 2024.
Supportive government incentives and funding for the development of charging infrastructure are driving market growth.
Leading companies in the market include Tesla, Electrify, EVgo, and ChargePoint.
The U.S. dominated the North America market in 2024.
Related Reports
-
US +1 833 909 2966 ( Toll Free )
-
Get In Touch With Us


